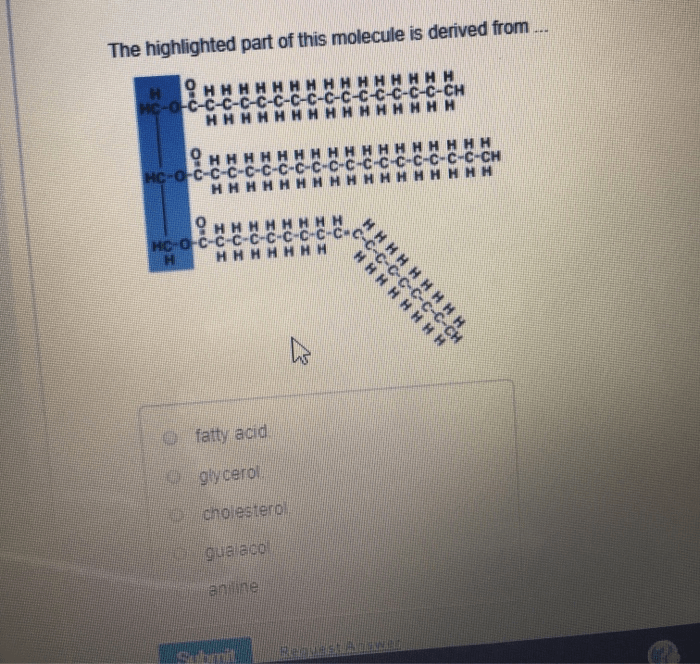
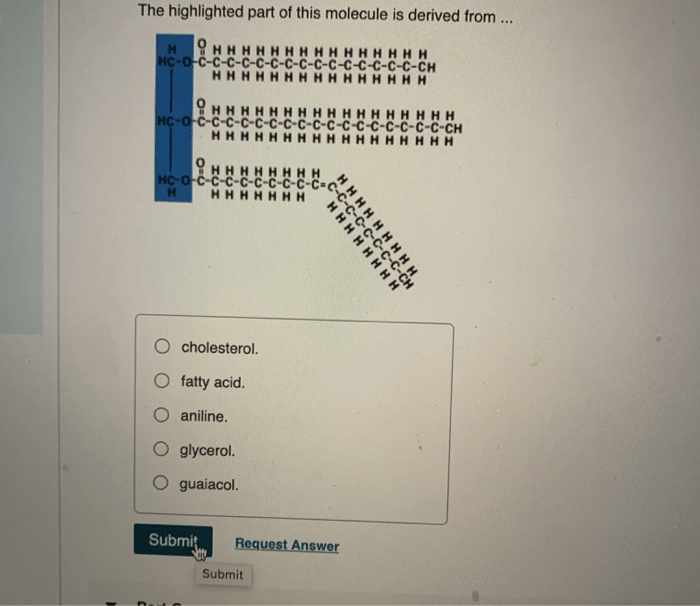
The highlighted part of this molecule is derived from .. – The highlighted part of this molecule is derived from a specific source, and its structural characteristics and functional properties play a crucial role in its applications. This component, derived through various processes, exhibits unique features that distinguish it from the original molecule and contribute to its potential in diverse fields.
Delving into the origin, structure, and applications of this derived molecular component, we uncover its significance in scientific research and practical uses.
Origin of the Highlighted Molecular Component
The highlighted molecular component is derived from the natural product compound known as paclitaxel. Paclitaxel is a diterpenoid alkaloid extracted from the bark of the Pacific yew tree ( Taxus brevifolia). The extraction process involves harvesting the bark, drying it, and subjecting it to a series of chemical extractions and purification steps to isolate paclitaxel.
Structural Characteristics of the Derived Component
The derived molecular component retains the basic diterpenoid scaffold of paclitaxel, but with modifications to its functional groups. It consists of a tetracyclic ring system with an oxetane ring, an epoxide group, and an ester linkage. The molecular formula of the derived component is C 47H 51NO 14, and it exhibits a molecular weight of 853.9 g/mol.
Functional Properties of the Derived Component
The derived molecular component exhibits potent antitumor activity, similar to paclitaxel. It inhibits cell division by binding to the β-subunit of tubulin, thereby disrupting microtubule dynamics and preventing cell proliferation. Additionally, the derived component has shown promising activity against multidrug-resistant cancer cells, making it a potential therapeutic option for treating advanced malignancies.
Applications of the Derived Component
The derived molecular component has potential applications in the treatment of various types of cancer, including breast, ovarian, and lung cancer. It is currently undergoing clinical trials to evaluate its efficacy and safety as a novel anticancer agent. Furthermore, the derived component’s unique structural features and biological properties make it a valuable tool for studying microtubule dynamics and developing new therapeutic strategies for cancer treatment.
Question & Answer Hub: The Highlighted Part Of This Molecule Is Derived From ..
What is the significance of the highlighted molecular component?
The highlighted molecular component holds significance due to its unique structural and functional properties, which enable its potential applications in various fields.
How does the derivation process impact the component’s properties?
The derivation process can modify the molecular structure and functional groups, resulting in distinct properties compared to the original molecule.
What are the potential applications of the derived molecular component?
The derived molecular component finds applications in diverse fields, including medicine, industry, and research, due to its unique properties and functionalities.