Which of the following exemplifies a personality trait – Delving into the realm of personality traits, this discourse unveils the intricate tapestry of human characteristics, unraveling the complexities that define our individuality. We embark on a journey to explore the multifaceted nature of personality, examining its manifestations, interrelationships, and the methods employed to measure its elusive essence.
Personality traits, the enduring dispositions that shape our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, provide a lens through which we can decipher the enigmatic puzzle of human nature. From the gregarious extrovert to the introspective introvert, the meticulous perfectionist to the carefree bohemian, each personality trait adds a unique brushstroke to the canvas of our existence.
Defining Personality Traits: Which Of The Following Exemplifies A Personality Trait
Personality traits are enduring psychological characteristics that influence an individual’s behavior, thoughts, and emotions. They are relatively stable over time and across situations, and they form the foundation of an individual’s unique personality.
Common personality traits include:
- Extroversion: A tendency to be outgoing, sociable, and assertive.
- Neuroticism: A tendency to experience negative emotions, such as anxiety, fear, and depression.
- Agreeableness: A tendency to be cooperative, friendly, and trusting.
- Conscientiousness: A tendency to be organized, responsible, and hardworking.
- Openness to Experience: A tendency to be curious, imaginative, and creative.
There are various models and theories that attempt to explain the structure and dynamics of personality traits. One of the most influential models is the Five-Factor Model (FFM), which proposes that personality can be described in terms of five broad traits: extroversion, neuroticism, agreeableness, conscientiousness, and openness to experience.
Identifying Exemplary Traits
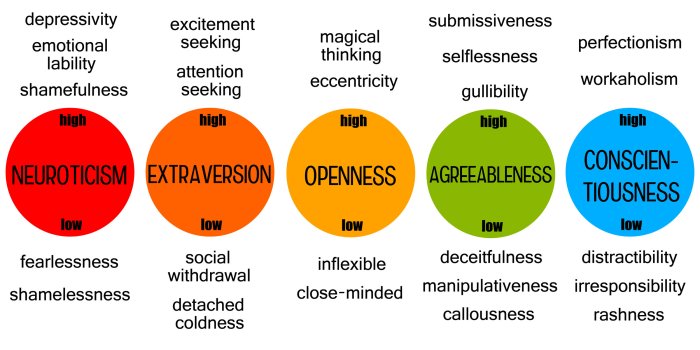
| Trait | Description | Example | Non-Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extroversion | Outgoing, sociable, talkative | Attending social events, making new friends | Avoiding social interactions, preferring solitude |
| Neuroticism | Tendency to experience negative emotions | Feeling anxious or stressed in social situations | Remaining calm and composed under pressure |
| Agreeableness | Cooperative, friendly, trusting | Helping others in need, compromising in conflicts | Being selfish, untrustworthy, hostile |
| Conscientiousness | Organized, responsible, hardworking | Setting goals, meeting deadlines, completing tasks | Being disorganized, procrastinating, neglecting responsibilities |
| Openness to Experience | Curious, imaginative, creative | Trying new things, seeking out novel experiences | Being closed-minded, resistant to change, unimaginative |
Analyzing Trait Manifestations
Personality traits can manifest in behavior in various ways. For example, an extroverted individual may be more likely to initiate conversations and participate in social activities, while a neurotic individual may be more likely to experience anxiety and worry.
The expression of traits can also be influenced by environmental factors. For example, an extroverted individual may be less likely to express their extroversion in a situation that is perceived as threatening or uncomfortable.
Trait Interrelationships

- Extroversion is often associated with agreeableness and openness to experience.
- Neuroticism is often associated with conscientiousness and introversion.
- Agreeableness is often associated with conscientiousness and openness to experience.
- Conscientiousness is often associated with extroversion and agreeableness.
- Openness to experience is often associated with extroversion and agreeableness.
The combination of certain traits can have potential consequences. For example, a highly extroverted and neurotic individual may be more likely to experience social anxiety, while a highly conscientious and agreeable individual may be more likely to be successful in their career.
Trait Measurement and Assessment
There are various methods used to measure and assess personality traits. One common method is self-report questionnaires, in which individuals answer questions about their own personality characteristics. Another method is observer ratings, in which trained observers rate an individual’s personality traits based on their behavior.
Different assessment tools have their own strengths and limitations. Self-report questionnaires are relatively easy to administer and can provide a broad overview of an individual’s personality. However, they are susceptible to response biases, such as social desirability bias.
Observer ratings can provide more objective assessments of personality traits. However, they are more time-consuming and expensive to administer, and they may be influenced by the observer’s own biases.
FAQ Insights
What is the difference between a personality trait and a personality type?
Personality traits are specific, measurable characteristics that describe an individual’s consistent patterns of thought, feeling, and behavior, while personality types are broader categories that group individuals based on their overall personality characteristics.
How are personality traits measured?
Personality traits can be measured using a variety of methods, including self-report questionnaires, observer ratings, and behavioral assessments.
Can personality traits change over time?
While personality traits are generally stable over time, they can change in response to significant life events or experiences.