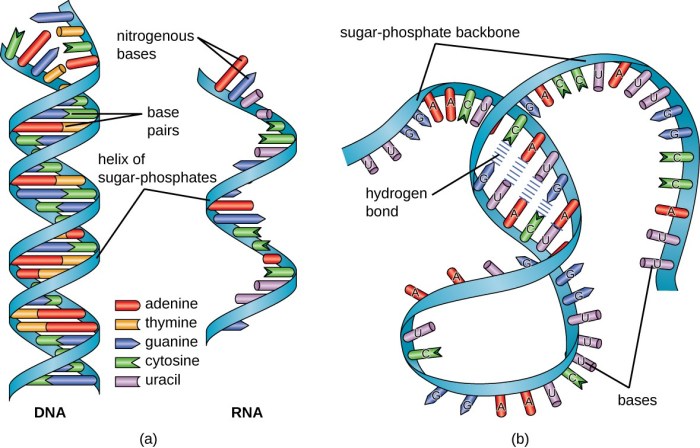
Match the form of rna with its function microrna – Match the form of RNA with its function: Microrna. Microrna is a small, non-coding RNA molecule that plays a crucial role in gene regulation. It targets and regulates mRNA molecules, thereby controlling gene expression. This article provides a comprehensive overview of microrna, its functions, classification, biogenesis, and its role in disease.
The discovery of microrna has revolutionized our understanding of gene regulation. Microrna molecules are found in all eukaryotes, and they are involved in a wide range of cellular processes, including development, differentiation, and metabolism. Dysregulation of microrna has been linked to various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Microrna Overview
Microrna (miRNA) are small, non-coding RNA molecules that play a crucial role in regulating gene expression. They are typically 20-22 nucleotides in length and are generated from longer RNA precursors through a complex biogenesis process. miRNAs are highly conserved across species, indicating their fundamental importance in biological processes.
The discovery of miRNAs in the early 2000s revolutionized our understanding of gene regulation. They were initially identified as regulators of developmental timing in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegansand have since been found to be involved in a wide range of cellular processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis.
Microrna Function
miRNAs primarily function by targeting and regulating messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. They bind to the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of mRNA through complementary base pairing, which can either inhibit translation or promote mRNA degradation.
miRNAs can also regulate gene expression by interacting with other RNA molecules, such as long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs). These interactions can influence the stability, localization, and translation of target mRNAs.
Microrna Classification, Match the form of rna with its function microrna
| Class | Sequence | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Canonical miRNAs | Typically 20-22 nucleotides in length | Target and regulate mRNA molecules |
| IsomiRs | miRNAs with slight variations in sequence | May have different target specificities |
| Star-strands | miRNAs derived from the opposite arm of the miRNA precursor | Can also have regulatory functions |
| piRNAs | Longer miRNAs (26-31 nucleotides) | Involved in germline development and transposon silencing |
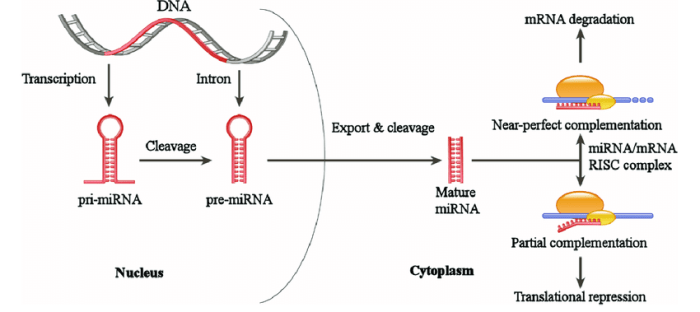
Microrna Biogenesis
miRNAs are generated through a multi-step biogenesis process that involves several enzymes and protein complexes:
- Transcription:miRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II into primary miRNA (pri-miRNA) transcripts.
- Processing:The pri-miRNA is processed by the Drosha-DGCR8 complex to form a shorter hairpin-shaped precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA).
- Export:The pre-miRNA is exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm by Exportin-5.
- Dicing:The pre-miRNA is cleaved by the Dicer-TRBP complex to form a mature miRNA duplex.
- Strand selection:One strand of the miRNA duplex (the guide strand) is selected and incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC).
Microrna and Disease
Dysregulation of miRNAs has been implicated in various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and cardiovascular diseases.
In cancer, miRNAs can act as either tumor suppressors or oncogenes. They can regulate cell proliferation, apoptosis, and metastasis by targeting key genes involved in these processes.
In neurodegenerative disorders, miRNAs have been found to play a role in neuronal development, synaptic plasticity, and neuroinflammation. Dysregulation of miRNAs can contribute to the pathogenesis of diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
FAQ Overview: Match The Form Of Rna With Its Function Microrna
What is microrna?
Microrna is a small, non-coding RNA molecule that plays a crucial role in gene regulation.
How does microrna regulate gene expression?
Microrna targets and regulates mRNA molecules, thereby controlling gene expression.
What is the role of microrna in disease?
Dysregulation of microrna has been linked to various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders.