Only insider threat indicators observed during – Insider threat indicators observed during are critical signs that an insider may be planning or carrying out malicious activities within an organization. These indicators can manifest in various forms, from subtle behavioral changes to overt actions, and it is crucial for organizations to be aware of them to mitigate potential risks.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the specific insider threat indicators observed during, providing examples and explaining their significance. It will also discuss methods used to detect and monitor these indicators, as well as the impact of insider threats on organizations and effective strategies for prevention and mitigation.
1. Insider Threat Indicators Observed During

Insider threats pose significant risks to organizations due to the privileged access and knowledge of insiders. Identifying and monitoring specific indicators can help mitigate these risks.
Some common insider threat indicators include:
- Unauthorized access to sensitive data or systems
- Excessive downloads or printing of confidential information
- Changes to system configurations or security settings without authorization
- Unusual or unexpected network activity
- Attempts to disable or bypass security controls
These indicators are significant because they suggest potential malicious intent or compromise. Detecting and monitoring them requires a combination of technical tools, such as intrusion detection systems and data loss prevention tools, as well as human analysis and behavioral monitoring.
2. Impact of Insider Threats
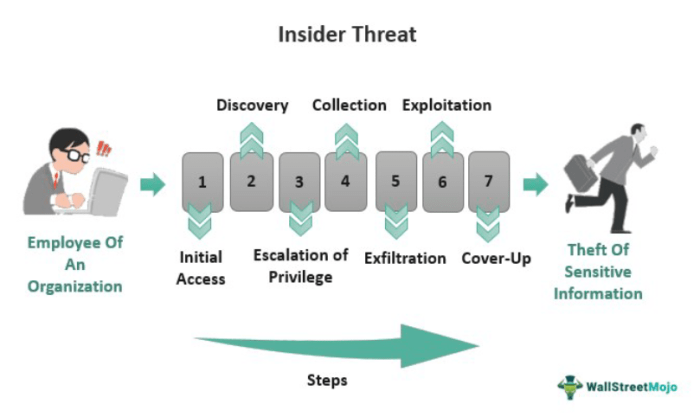
Insider threats can have devastating consequences for organizations. They can compromise data security, disrupt operations, and damage reputation.
Data security breaches caused by insiders can result in the loss or theft of sensitive information, leading to financial losses, regulatory fines, and reputational damage. Insider threats can also disrupt operations by sabotaging systems or stealing critical data, causing productivity losses and business interruptions.
Furthermore, insider threats can erode trust and damage an organization’s reputation. Customers, partners, and employees may lose confidence in an organization that has been compromised by an insider, leading to decreased revenue and increased legal liability.
3. Prevention and Mitigation Strategies

Preventing and mitigating insider threats requires a multi-layered approach involving technology, policy, and human factors.
Security awareness training can educate employees about insider threats and the importance of protecting sensitive information. Access controls, such as role-based permissions and two-factor authentication, can restrict access to sensitive data and systems.
Monitoring systems can detect unusual or suspicious activity, such as unauthorized access attempts or data exfiltration. Creating a culture of trust and open communication can encourage employees to report suspicious behavior or concerns, fostering a sense of collective responsibility.
FAQ Resource: Only Insider Threat Indicators Observed During
What are some common insider threat indicators observed during?
Common insider threat indicators include unauthorized access to sensitive data, changes in behavior or mood, financial difficulties, and personal grievances.
How can organizations detect and monitor insider threat indicators?
Organizations can detect and monitor insider threat indicators through security awareness training, access controls, monitoring systems, and data analytics.
What are the potential consequences of insider threats?
Insider threats can compromise data security, disrupt operations, damage reputation, and result in financial and legal implications.
