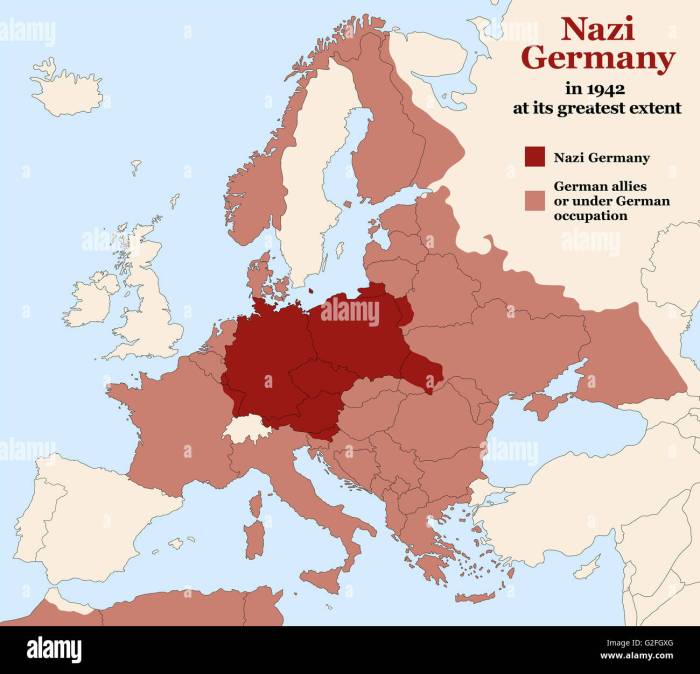
The third reich based its power primarily onfear.censorship.laws.incentive. – The Third Reich’s ascent to power was intricately intertwined with its systematic implementation of fear, censorship, legal manipulation, and incentives. This comprehensive analysis delves into the strategies employed by the Nazi regime to establish and maintain its iron grip on Germany.
Through a meticulous examination of historical accounts and scholarly research, this discourse unveils the chilling tactics used to instill terror, silence dissent, manipulate laws, and reward compliance. It offers a profound understanding of the insidious methods that enabled the Third Reich to consolidate its authority and suppress any semblance of resistance.
1. Fear as a Tool of Power: The Third Reich Based Its Power Primarily Onfear.censorship.laws.incentive.
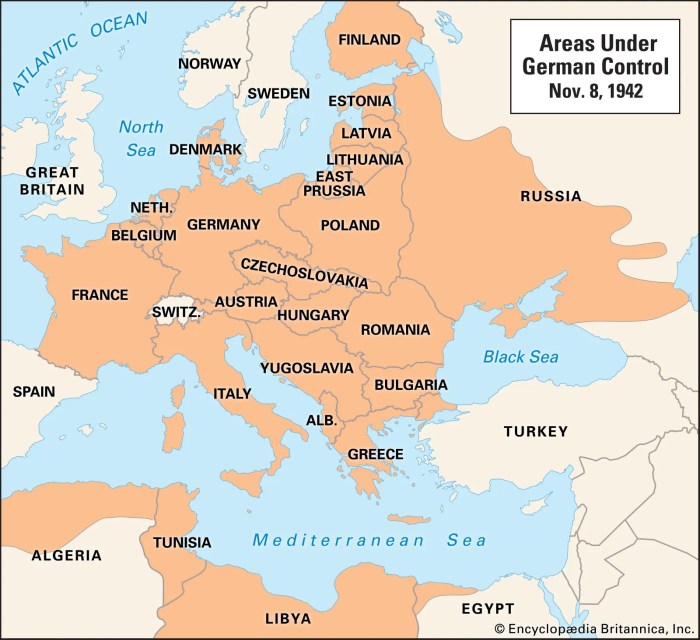
The Third Reich used fear as a primary means of control, instilling terror in its citizens to ensure obedience and suppress dissent. This climate of fear was created through various methods:
Methods of Instilling Fear, The third reich based its power primarily onfear.censorship.laws.incentive.
- Secret Police (Gestapo):The Gestapo ruthlessly pursued and arrested anyone suspected of opposing the regime, spreading a constant sense of surveillance and paranoia.
- Concentration Camps:The establishment of concentration camps served as a stark warning of the consequences of resistance, with prisoners subjected to unimaginable horrors.
- Public Executions:Executions were staged in public to send a clear message that any act of defiance would be met with severe punishment.
- Propaganda:Nazi propaganda portrayed Jews and other “enemies of the state” as threats to the German people, creating a pervasive sense of fear and distrust.
Effectiveness of Fear
The regime’s use of fear was highly effective in controlling the population. Citizens lived in constant dread of being targeted by the Gestapo or sent to concentration camps. This fear stifled any potential resistance and ensured that the vast majority of Germans remained compliant.
2. Censorship and the Suppression of Dissent

The Third Reich imposed strict censorship to suppress any form of dissent or criticism. This censorship extended to all forms of media:
Targets of Censorship
- Books and Publications:Books and newspapers were heavily censored, with any content deemed subversive or critical of the regime being banned.
- Film and Theater:Films and theatrical productions were closely monitored, and any work that did not conform to Nazi ideology was prohibited.
- Radio and Television:Radio and television broadcasts were tightly controlled, with only government-approved content being aired.
- Art and Music:Artistic expression was also subject to censorship, with modern and abstract art being condemned as “degenerate.”
Commonly Asked Questions
How did the Third Reich instill fear in its citizens?
The Nazi regime employed a systematic campaign of terror through the Gestapo, SS, and concentration camps. They used arbitrary arrests, torture, and public executions to create a climate of fear and silence dissent.
What were the targets of censorship during the Third Reich?
Censorship under the Nazis extended to all forms of media, including books, newspapers, films, and radio broadcasts. It targeted anything deemed critical of the regime, including political opponents, religious groups, and ethnic minorities.
How did the Third Reich manipulate laws to consolidate its power?
The Nazis passed a series of laws, such as the Enabling Act of 1933, which granted Hitler dictatorial powers. They also suspended civil liberties, violated constitutional rights, and established a system of arbitrary justice.
What incentives were offered by the Third Reich to encourage compliance?
The Nazis used a combination of rewards and punishments to gain support and loyalty. They offered economic benefits, social privileges, and career opportunities to those who supported the regime, while ostracizing and persecuting those who resisted.