A ball is thrown horizontally at a speed of 24 – A ball thrown horizontally at a speed of 24 m/s embarks on a captivating journey, influenced by the interplay of velocity, acceleration, and displacement. This exploration delves into the trajectory of the ball, examining its shape and path while considering the factors that mold its motion.
As the ball soars through the air, we dissect its horizontal and vertical components of velocity, unraveling their impact on its movement in the x and y directions. The effects of air resistance and drag come under scrutiny, revealing how these forces shape the ball’s velocity and trajectory.
Physics Concepts
When a ball is thrown horizontally, it experiences two main types of motion: horizontal motion and vertical motion. Horizontal motion is the motion of the ball in the direction it was thrown, while vertical motion is the motion of the ball up and down due to the force of gravity.
The velocity of the ball is a vector quantity that describes both the speed and direction of the ball’s motion. The acceleration of the ball is a vector quantity that describes the rate at which the ball’s velocity is changing.
The displacement of the ball is a vector quantity that describes the change in the ball’s position.
Relationship between Velocity, Acceleration, and Displacement, A ball is thrown horizontally at a speed of 24
The velocity, acceleration, and displacement of the ball are related by the following equations:
- v = u + at
- a = (v – u) / t
- s = ut + 1/2 at^2
where:
- v is the final velocity
- u is the initial velocity
- a is the acceleration
- t is the time
- s is the displacement
Trajectory of the Ball
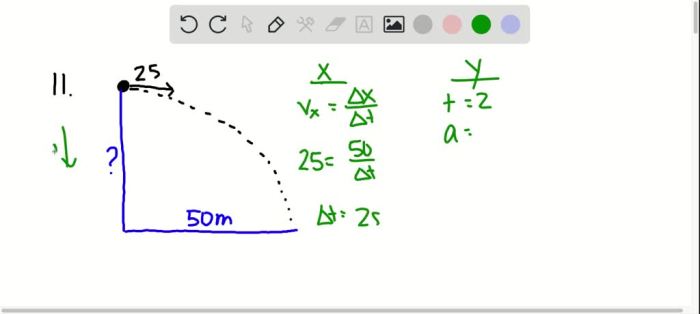
The trajectory of the ball is the path that the ball follows through the air. The shape of the trajectory is a parabola. The ball’s initial velocity and the force of gravity determine the path of the trajectory.
Factors Influencing the Trajectory
- Initial velocity: The higher the initial velocity, the longer the ball will travel horizontally before it begins to fall.
- Force of gravity: The force of gravity pulls the ball down towards the ground, causing it to fall.
Diagram of the Trajectory
[Diagram of the trajectory of a ball thrown horizontally]
Horizontal and Vertical Components of Velocity: A Ball Is Thrown Horizontally At A Speed Of 24
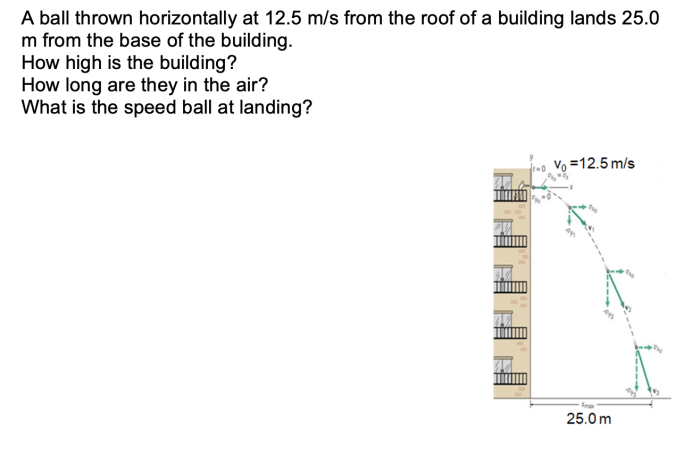
The velocity of the ball can be broken down into two components: horizontal velocity and vertical velocity. The horizontal velocity is the component of the velocity that is parallel to the ground. The vertical velocity is the component of the velocity that is perpendicular to the ground.
Effect on the Motion of the Ball
The horizontal velocity of the ball determines how far the ball will travel horizontally before it begins to fall. The vertical velocity of the ball determines how high the ball will rise before it begins to fall.
Diagram of the Horizontal and Vertical Components of Velocity
[Diagram of the horizontal and vertical components of velocity of a ball thrown horizontally]
Air Resistance and Drag
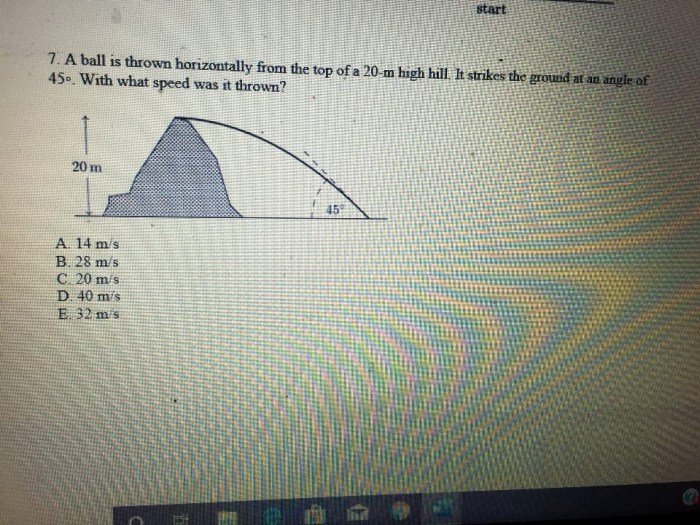
Air resistance is a force that opposes the motion of the ball through the air. Drag is a type of air resistance that is caused by the shape of the ball.
Effects on the Motion of the Ball
- Air resistance slows down the ball.
- Drag causes the ball to fall more quickly.
Diagram of the Effects of Air Resistance and Drag
[Diagram of the effects of air resistance and drag on a ball thrown horizontally]
Range and Height of the Ball
The range of the ball is the horizontal distance that the ball travels before it hits the ground. The height of the ball is the vertical distance that the ball travels before it reaches its maximum height.
Factors Influencing the Range and Height
- Initial velocity: The higher the initial velocity, the greater the range and height of the ball.
- Force of gravity: The force of gravity pulls the ball down towards the ground, reducing its range and height.
Diagram of the Range and Height of the Ball
[Diagram of the range and height of a ball thrown horizontally]
FAQ Summary
What is the initial velocity of the ball?
24 m/s
What is the shape of the ball’s trajectory?
A parabola
What factors influence the range of the ball?
Initial velocity, angle of projection, and air resistance