Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of molecular biology with our comprehensive DNA and RNA Practice Worksheet Answer Key. This invaluable resource empowers students to delve into the intricacies of DNA and RNA structure, function, and their pivotal role in genetic information storage and protein synthesis.
Through a lucid and engaging narrative, we unravel the complexities of DNA replication, transcription, and translation, shedding light on the fundamental processes that govern cellular life. Explore the groundbreaking techniques of DNA technology, unlocking its vast applications in medicine, biotechnology, and beyond.
DNA Structure
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule that contains the instructions for an organism’s development and characteristics. It is found in the nucleus of cells and is made up of two long strands of nucleotides.
Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The sequence of these bases along the DNA strand determines the genetic code for an organism.
Differences between DNA and RNA
- DNA is double-stranded, while RNA is single-stranded.
- DNA contains the sugar molecule deoxyribose, while RNA contains the sugar molecule ribose.
- DNA contains the nitrogenous base thymine, while RNA contains the nitrogenous base uracil.
Role of DNA in genetic information storage
DNA is responsible for storing the genetic information that is passed from parents to offspring. This information is used to direct the development and function of an organism.
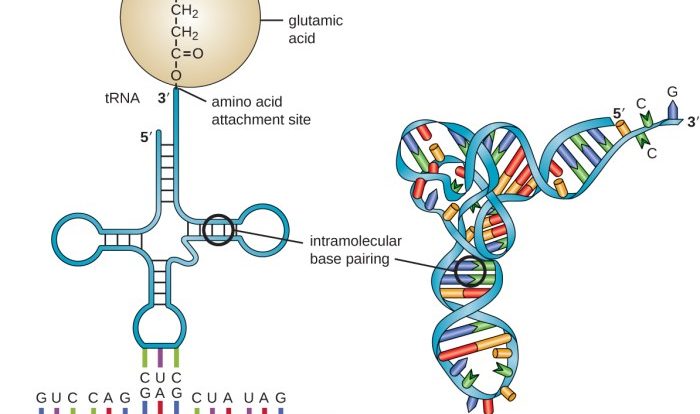
RNA Structure and Function
RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a molecule that is involved in protein synthesis. It is found in the cytoplasm of cells and is made up of a single strand of nucleotides.
Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases are adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
Types of RNA and their functions
- Messenger RNA (mRNA)carries the genetic code from the nucleus to the ribosomes, where proteins are made.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA)brings amino acids to the ribosomes in the correct order to build proteins.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)is a component of ribosomes and helps to catalyze the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids.
Role of RNA in protein synthesis
RNA is essential for protein synthesis. It carries the genetic code from the nucleus to the ribosomes, where proteins are made. The ribosomes use the tRNA to bring amino acids to the correct order to build proteins.
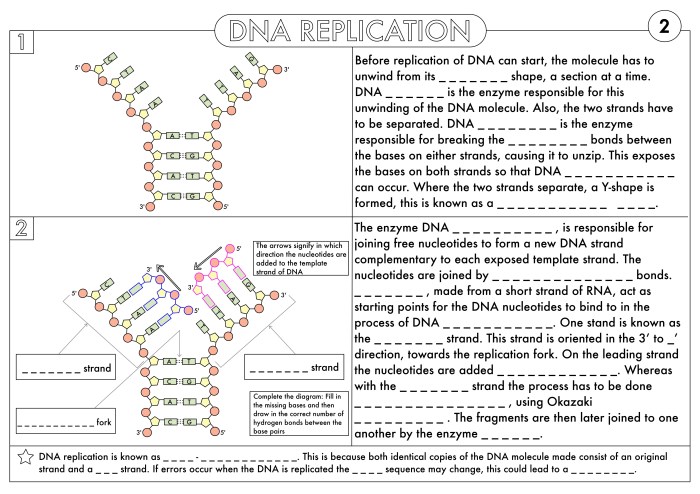
DNA Replication: Dna And Rna Practice Worksheet Answer Key
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes a copy of its DNA before cell division. This process is essential for the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
Enzymes involved in DNA replication
- Helicaseunwinds the DNA double helix.
- DNA polymeraseadds new nucleotides to the growing DNA strand.
- Ligasejoins the newly synthesized DNA strands together.
Importance of DNA replication for cell division
DNA replication is essential for cell division. It ensures that each new cell receives a complete copy of the DNA, which is necessary for the cell to function properly.
Transcription and Translation
Transcription
Transcription is the process by which the genetic code in DNA is copied into RNA. This process occurs in the nucleus of cells.
The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to the DNA and separates the two strands. RNA polymerase then uses the DNA strand as a template to synthesize a complementary RNA strand.
Translation
Translation is the process by which the genetic code in RNA is used to build proteins. This process occurs in the cytoplasm of cells.
The ribosome binds to the RNA and reads the genetic code. The ribosome then uses the tRNA to bring amino acids to the correct order to build proteins.
Gene Expression
Regulation of gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which the information in a gene is used to make a protein. This process is regulated by a number of factors, including:
- Transcription factors
- Enhancers
- Silencers
Role of transcription factors in gene expression, Dna and rna practice worksheet answer key
Transcription factors are proteins that bind to DNA and regulate the transcription of genes. Transcription factors can either activate or repress gene expression.
DNA Technology
DNA technology is a set of techniques that are used to manipulate and analyze DNA. These techniques have a wide range of applications in medicine, biotechnology, and forensic science.
Applications of DNA technology in medicine and biotechnology
- Diagnosis and treatment of genetic diseases
- Development of new drugs and vaccines
- Gene therapy
Ethical implications of DNA technology
DNA technology has a number of ethical implications, including:
- Privacy concerns
- Discrimination
- Eugenics
FAQ Compilation
What is the primary function of DNA?
DNA serves as the blueprint for genetic information, carrying the instructions necessary for the development and functioning of organisms.
How does RNA differ from DNA?
RNA is a single-stranded molecule that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis, carrying genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes.
What is the significance of DNA replication?
DNA replication ensures the accurate duplication of genetic material during cell division, ensuring the faithful transmission of genetic information to daughter cells.