In the intricate tapestry of the nervous system, neuroglial cells play a vital role. Match the neuroglial cell with its function to embark on a journey of discovery, unraveling the intricate mechanisms that govern neural communication and homeostasis.
Neuroglial cells, often referred to as the “glue” of the nervous system, are a diverse group of non-neuronal cells that provide essential support for the proper functioning of neurons. From maintaining homeostasis to facilitating nerve impulse transmission, these cells are indispensable for the seamless operation of our cognitive and motor abilities.
Neuroglial Cells
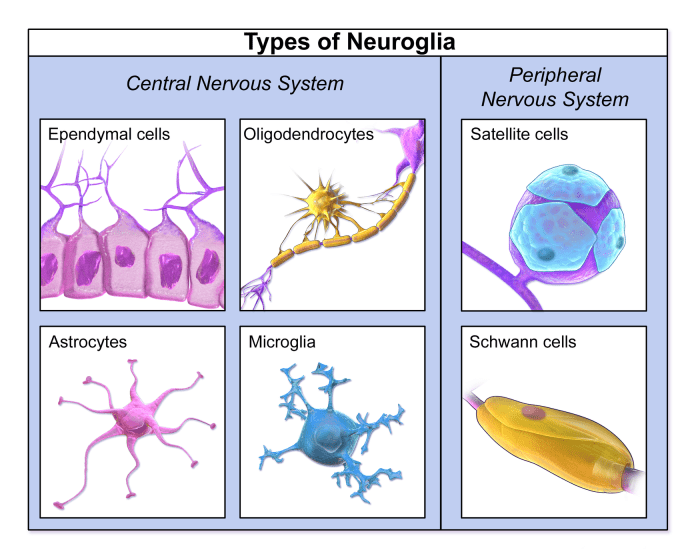
Neuroglial cells, also known as glial cells, are non-neuronal cells that play a vital role in the nervous system. They provide structural support, nourishment, and protection to neurons, and they contribute to the overall function of the nervous system.Neuroglial cells are divided into several types, each with a specific function.
The major types of neuroglial cells include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells, and Schwann cells.
Astrocytes
Astrocytes are the most abundant type of neuroglial cell. They are star-shaped cells with a large number of processes that extend in all directions. Astrocytes have several important functions, including:
- Maintaining the blood-brain barrier, which regulates the entry of substances from the blood into the brain.
- Providing nutrients to neurons.
- Regulating neurotransmission by releasing chemical messengers that can influence the activity of neurons.
- Repairing damaged tissue in the nervous system.
Oligodendrocytes, Match the neuroglial cell with its function
Oligodendrocytes are responsible for myelinating axons in the central nervous system. Myelin is a fatty substance that insulates axons and speeds up the transmission of nerve impulses. Oligodendrocytes extend processes that wrap around axons, forming a myelin sheath.
- Each oligodendrocyte can myelinate multiple axons.
- Myelination is essential for the proper function of the nervous system.
- Damage to oligodendrocytes can lead to demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
Microglia
Microglia are the immune cells of the nervous system. They are constantly surveying the brain and spinal cord for signs of infection or injury. When they detect a problem, they become activated and release chemicals that can kill pathogens or damaged cells.
- Microglia are also involved in the development and pruning of the nervous system.
- They play a role in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
Questions Often Asked: Match The Neuroglial Cell With Its Function
What is the primary function of astrocytes?
Astrocytes are responsible for maintaining homeostasis in the neural environment, providing nutrients to neurons, and regulating neurotransmission.
How do oligodendrocytes contribute to nerve impulse transmission?
Oligodendrocytes myelinate axons in the central nervous system, facilitating faster and more efficient nerve impulse transmission.
What is the role of microglia in the nervous system?
Microglia act as the immune cells of the nervous system, removing debris, responding to injury, and providing immune surveillance.

