Unveiling the intricacies of protein synthesis, this protein synthesis worksheet with answers embarks on an illuminating journey through the fundamental processes that govern the very essence of life. Delving into the molecular realm, we unravel the intricate interplay of DNA, RNA, and ribosomes, shedding light on the remarkable symphony that orchestrates the production of proteins, the workhorses of our biological machinery.
From the blueprints of DNA to the assembly line of ribosomes, we dissect the mechanisms that translate genetic information into functional proteins, exploring the nuances of transcription, translation, and the genetic code. With a keen eye on structure and function, we delve into the hierarchical organization of proteins, unraveling the intricate relationship between their architecture and their diverse roles within the cellular landscape.
Protein Synthesis Overview: Protein Synthesis Worksheet With Answers
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells create proteins. Proteins are essential for life and perform a wide range of functions, including:
- Providing structural support
- Transporting molecules
- Catalyzing reactions
- Regulating gene expression
Protein synthesis is a complex process that involves three main steps:
- Transcription: The DNA sequence of a gene is copied into a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule.
- Translation: The mRNA molecule is translated into a chain of amino acids, which form the protein.
- Protein folding: The amino acid chain folds into a specific shape, which determines the protein’s function.
Transcription, Protein synthesis worksheet with answers
Transcription is the process of copying the DNA sequence of a gene into an mRNA molecule. This process is carried out by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. RNA polymerase binds to the DNA at a specific location called the promoter.
It then moves along the DNA, unwinding the double helix and copying the sequence of bases into an mRNA molecule.
Translation
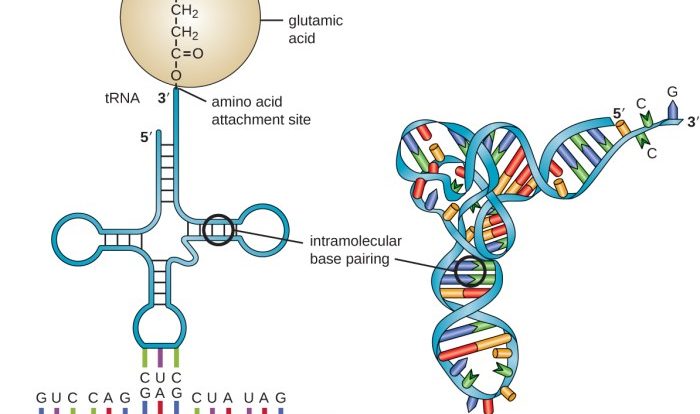
Translation is the process of translating the mRNA molecule into a chain of amino acids. This process is carried out by ribosomes. Ribosomes are large, complex structures that are composed of RNA and protein. Ribosomes bind to the mRNA molecule at a specific location called the start codon.
They then move along the mRNA molecule, reading the sequence of bases three at a time. Each three-base sequence, called a codon, corresponds to a specific amino acid. The ribosome uses this information to add the correct amino acid to the growing chain of amino acids.
Protein Structure and Function
The structure of a protein is determined by the sequence of amino acids in the chain. There are four levels of protein structure:
- Primary structure: The sequence of amino acids in the chain.
- Secondary structure: The way in which the amino acid chain folds into a regular pattern, such as an alpha helix or a beta sheet.
- Tertiary structure: The way in which the secondary structure folds into a specific three-dimensional shape.
- Quaternary structure: The way in which multiple protein chains come together to form a complex.
The structure of a protein is essential for its function. The shape of the protein determines its ability to bind to other molecules and to carry out its specific role.
Protein Synthesis Regulation
Protein synthesis is a tightly regulated process. This regulation is essential to ensure that cells produce the right proteins at the right time. There are a number of different mechanisms that regulate protein synthesis, including:
- Transcription factors: Transcription factors are proteins that bind to the promoter of a gene and either activate or repress transcription.
- Translational repressors: Translational repressors are proteins that bind to mRNA molecules and prevent them from being translated.
- MicroRNAs: MicroRNAs are small RNA molecules that bind to mRNA molecules and cause them to be degraded.
Common Queries
What is the role of ribosomes in protein synthesis?
Ribosomes serve as the molecular machinery responsible for translating the genetic code into a chain of amino acids, forming the polypeptide backbone of proteins.
How does the genetic code determine the sequence of amino acids in a protein?
The genetic code, a set of three-nucleotide codons, specifies the order of amino acids in a protein. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid or a stop signal.
What are the different levels of protein structure?
Protein structure is organized hierarchically into four levels: primary (amino acid sequence), secondary (local folding patterns), tertiary (overall 3D structure), and quaternary (interactions between multiple protein subunits).