Qi 105 leading quality improvement – Embark on a journey of transformative healthcare quality improvement with QI 105. This comprehensive guide unveils the significance, principles, and strategies behind QI 105, empowering you to harness its potential for enhancing patient outcomes and optimizing healthcare delivery.
Discover the essential tools, techniques, and data analysis methodologies that drive successful QI 105 implementation. Explore real-world case studies showcasing the tangible impact of QI 105 in healthcare settings, inspiring you to embrace this transformative approach.
QI 105 Leading Quality Improvement
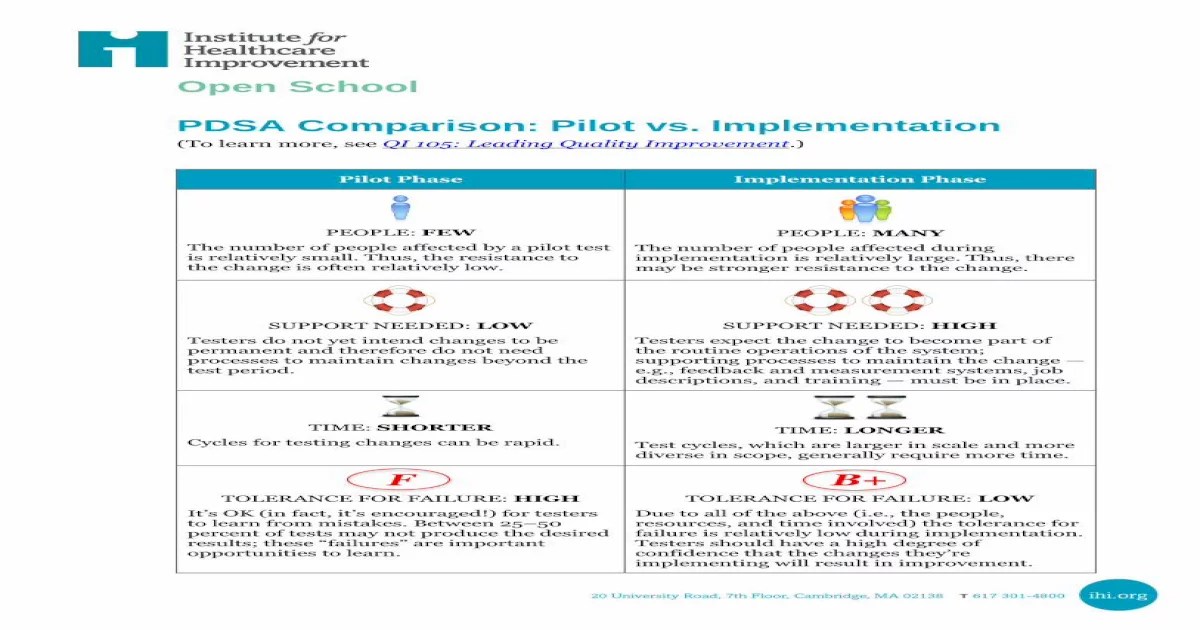
QI 105 Leading Quality Improvement is a foundational standard in healthcare quality management, providing a systematic approach to enhance patient care and organizational performance.
Its key principles center around creating a culture of continuous improvement, involving all stakeholders, and utilizing data-driven decision-making to drive quality initiatives.
Significance of QI 105 in Healthcare
- Enhances patient safety and outcomes by reducing errors and improving care delivery.
- Improves operational efficiency, reducing costs and increasing productivity.
- Promotes staff engagement and satisfaction by empowering them in quality improvement initiatives.
- Supports regulatory compliance and accreditation, demonstrating commitment to quality and patient safety.
Key Principles and Concepts of QI 105
QI 105 emphasizes several core principles:
- Patient-Centered Care:Focuses on improving outcomes and experiences for patients.
- Continuous Improvement:Encourages ongoing evaluation and refinement of processes to enhance quality.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making:Utilizes data to identify areas for improvement and track progress.
- Stakeholder Involvement:Engages patients, staff, leaders, and other stakeholders in quality improvement efforts.
- Systemic Approach:Addresses quality improvement at the organizational level, considering all interconnected processes.
QI 105 Implementation Strategies
Implementing QI 105 in healthcare organizations requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses several strategies. These strategies aim to establish a culture of continuous improvement, engage stakeholders, and ensure the effective utilization of QI 105 tools and methodologies.
Best practices for successful implementation include:
- Leadership Commitment:Securing buy-in and support from leadership is crucial for creating an environment conducive to QI initiatives.
- Stakeholder Engagement:Involving stakeholders from various levels and disciplines fosters a sense of ownership and accountability.
- Data-Driven Approach:Utilizing data to identify areas for improvement and track progress is essential for informed decision-making.
- Training and Education:Providing comprehensive training on QI 105 principles and methodologies empowers staff to actively participate in improvement efforts.
- Resource Allocation:Dedicating adequate resources, including time, personnel, and funding, ensures the sustainability of QI initiatives.
- Continuous Evaluation:Regularly assessing the effectiveness of QI 105 implementation allows for necessary adjustments and improvements.
QI 105 Tools and Techniques
QI 105 employs a comprehensive suite of tools and techniques to facilitate systematic quality improvement. These tools empower healthcare professionals to identify areas for improvement, develop and implement effective interventions, and monitor progress toward desired outcomes.
QI 105 tools and techniques are designed to promote collaboration, data-driven decision-making, and continuous improvement. By utilizing these tools, healthcare teams can enhance the quality and safety of patient care while optimizing processes and reducing costs.
Essential QI 105 Tools and Techniques
- Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) Cycle:A structured approach for testing and implementing changes, involving planning, implementing, studying the results, and making adjustments based on findings.
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA):A systematic process for identifying the underlying causes of a problem or issue, allowing for targeted interventions to address the root cause.
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA):A proactive technique for identifying potential failures and their consequences, enabling the development of strategies to mitigate risks and prevent adverse events.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC):A data-driven approach for monitoring and controlling processes to identify and reduce variation, ensuring consistent and reliable outcomes.
- Benchmarking:A process of comparing performance against internal or external standards to identify areas for improvement and best practices.
- Quality Improvement Teams:Collaborative groups responsible for leading and implementing quality improvement initiatives, leveraging diverse perspectives and expertise.
- Quality Improvement Software:Tools that support data collection, analysis, and reporting, facilitating data-driven decision-making and tracking progress.
How QI 105 Tools and Techniques Facilitate Quality Improvement
QI 105 tools and techniques provide a structured and systematic approach to quality improvement, enabling healthcare teams to:
- Identify and prioritize areas for improvement:Tools like RCA and FMEA help identify the root causes of problems, while benchmarking allows for comparison against best practices.
- Develop and implement effective interventions:PDSA cycles and quality improvement teams facilitate the testing and implementation of evidence-based interventions.
- Monitor and evaluate progress:SPC and quality improvement software enable ongoing monitoring of processes and outcomes, providing data for decision-making and course correction.
- Sustain improvements:Quality improvement teams and ongoing monitoring ensure that improvements are sustained and embedded into routine practice.
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement:QI 105 tools and techniques promote a data-driven and collaborative approach to quality improvement, fostering a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
QI 105 Data Analysis and Interpretation
Data analysis is a critical component of QI 105, enabling the identification of areas for improvement and driving effective decision-making. Through careful analysis of collected data, QI teams can gain valuable insights into the processes and outcomes they are seeking to enhance.
Understanding the Importance of Data Analysis in QI 105
Data analysis provides a structured and objective approach to evaluating QI initiatives. By examining data, teams can assess the effectiveness of interventions, identify patterns and trends, and pinpoint areas where improvements can be made. Data analysis helps to ensure that QI efforts are data-driven and based on evidence, rather than relying solely on subjective observations or assumptions.
Interpreting Data to Identify Areas for Improvement
Effective data interpretation involves understanding the meaning behind the numbers and extracting actionable insights. QI teams should consider the following steps when interpreting data:
- Examine trends and patterns:Look for changes over time, correlations between variables, and any outliers that may indicate areas for further investigation.
- Identify variations:Analyze data to identify any significant variations in processes or outcomes. These variations may indicate potential problems or opportunities for improvement.
- Compare to benchmarks:Benchmarking against industry standards or internal targets can provide valuable insights into areas where performance falls short or exceeds expectations.
- Consider the context:Data interpretation should take into account the specific context in which it was collected. Factors such as the patient population, resources available, and organizational culture may influence the interpretation.
By carefully analyzing and interpreting data, QI teams can gain a deep understanding of the processes they are evaluating and identify areas where improvements can be made, leading to better outcomes and enhanced quality of care.
QI 105 Case Studies: Qi 105 Leading Quality Improvement
QI 105 has been successfully implemented in various healthcare settings, leading to significant improvements in patient outcomes, efficiency, and cost reduction. Here are a few notable case studies that demonstrate the impact of QI 105 implementation:
Case Study: Reducing Hospital Readmissions, Qi 105 leading quality improvement
A study conducted in a large hospital system aimed to reduce hospital readmissions for patients with heart failure. The QI 105 methodology was used to identify root causes of readmissions, develop interventions, and implement a quality improvement plan. The interventions included enhanced patient education, medication reconciliation, and improved communication between providers and patients.
As a result, the readmission rate was reduced by 25%, leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Case Study: Improving Patient Satisfaction
A primary care clinic implemented QI 105 to improve patient satisfaction scores. The team used surveys to identify areas of dissatisfaction and developed interventions to address them. These interventions included implementing a patient portal, improving appointment scheduling, and providing personalized care plans.
As a result, patient satisfaction scores increased by 15%, indicating a significant improvement in patient experience.
Case Study: Reducing Surgical Site Infections
A surgical team used QI 105 to reduce surgical site infections. They identified risk factors for infections, developed a bundle of interventions, and implemented a quality improvement plan. The interventions included improved preoperative skin preparation, use of antibiotics, and enhanced surveillance.
As a result, the surgical site infection rate was reduced by 50%, demonstrating the effectiveness of QI 105 in improving surgical outcomes.
QI 105 Challenges and Opportunities
QI 105 implementation presents various challenges, including resource constraints, resistance to change, and data limitations. However, it also offers significant opportunities to improve healthcare quality and patient outcomes.
Overcoming these challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities requires a systematic approach, stakeholder engagement, and data-driven decision-making.
Challenges
Resource constraints:QI 105 implementation can require significant financial and human resources, which may be limited in healthcare organizations.
Resistance to change:Healthcare professionals may resist changes to their established practices, making QI 105 implementation challenging.
Data limitations:Accessing and analyzing accurate and timely data can be a barrier to effective QI 105 implementation.
Opportunities
Improved patient outcomes:QI 105 can lead to improved patient outcomes by identifying and addressing areas for improvement in healthcare delivery.
Reduced healthcare costs:By eliminating waste and improving efficiency, QI 105 can help reduce healthcare costs.
Enhanced patient satisfaction:QI 105 can improve patient satisfaction by involving patients in the quality improvement process.
FAQ Summary
What is the primary goal of QI 105?
QI 105 aims to provide a systematic framework for healthcare organizations to continuously improve the quality of care they deliver, with a focus on patient safety, effectiveness, and efficiency.
How does QI 105 differ from traditional quality improvement approaches?
QI 105 emphasizes a data-driven, collaborative, and iterative approach, involving all stakeholders in the healthcare delivery process. It promotes a culture of continuous learning and improvement, rather than relying solely on reactive measures.
What are the key benefits of implementing QI 105?
QI 105 implementation can lead to improved patient outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, increased staff satisfaction, and enhanced overall healthcare system performance.